Anxiety Explained in Different Psychological Perspectives
Anxiety disorders can promote a crippling focus upon negative life-events and make concentration difficult which can lead to. Generalized anxiety disorder GAD is a persistent excessive fearfulness and worry that lingers at.

Psychological Perspectives For Ap Psychology Albert Io
Because anxiety can be rated on a continuum some investigators suggest that extreme anxiety represents only a severe expression of the trait rather than a distinct or pathological state.
. Anxiety is often prompted by some sort of fear or stress factor that enters our life and results in a flight-or-fight physiological mode in. One biodynamic the other psychodynamic. Because of the existence of the life and death instincts and their unavoidable conflict Freud emphasised the inevitability of anxiety.
Anxiety disorders are a major worldwide health problem with sizeable psychological social and economic costs Beddington et al 2008. Research has identified four important psychological variables that predict a psychological vulnerability to anxiety. Social anxiety is also largely explained by cognitive theorists.
Parkinson Rachman 1981. In general NATs and worries represent appraisals of events in cognitive models of anxiety while obsessions are intrusive mental experiences that are the focus of appraisals. Anxiety is the leading cause of mental illness.
Anxiety disorders are common mental disorders characterized by frequent and excessive anxiety fear and distress. Freud put forward two theories of anxiety. This theory is especially interested in the dynamic relations between conscious and unconscious motivation and asserts.
Worries are normal phenomena Wells Morrison 1994 as are obsessions. Ad 90 of Clients Report Improvement in Anxiety Depression Symptoms After Two Sessions. The lifetime prevalence of anxiety disorders in the United States is approximately 30 percent of adults.
In a review of approximately 1600 at-risk cardiovascular patients. Beyond generalized anxiety disorder other. Safe Effective Science-Backed Treatment with Leaders in Clinical Psychiatry.
Mowrer Burrhus Skinner and Joseph Wolpe resulting. You may wonder why there are so many different psychology approaches and whether one approach is correct and others wrong. These two approaches should complement rather oppose one another.
It helps to explain the many different ways that people experience anxiety. According to SLT people with anxiety disorders may have learned to be anxious through prior contact with other people. What an Anxiety Diagnosis Means.
Obsessions occur as urges or impulses as well as thoughts eg. There are two different but not irreconcilable approaches to understanding the mechanisms of anxiety. As previously mentioned a person is more likely to develop an anxiety disorder if they are biologically predisposed to anxiety in conjunction with a psychological vulnerability.
During times of stress people often turn to unhealthy behaviors to alleviate anxiety. That anxiety is experienced when a person feels himself in impending danger. Using a humanist perspective a psychologist might look for ways to help people focus on more positive aspects of their experience rather than dwelling on negative emotions.
The perspective used in explaining a psychological disorder is extremely important in that it will consist of explicit assumptions regarding. Negative thought patterns a lack of exercise and consumption of empty calories often increase rather than diffuse anxious feelings and can contribute to ill health and depression. The five major perspectives in psychology are biological psychodynamic behavioral cognitive and humanistic.
This is a viewpoint shared by most theoretical persuasions but there is a particular vantage point which owes most to the psycho-analytical tradition established by Freud. Theories of anxiety looks at four key perspectives on anxiety. Anxiety plays an adaptive role in human development signaling that self-protective action is required to ensure safety.
Least 6 months and occurs more days than not. Psychodynamic theory is an approach to psychology that studies the psychological forces underlying human behavior feelings and emotions and how they may relate to early childhood experience. Firstly Freuds views on psychoanalysis.
Despite the lack of an actual threat the mind is forced to deal with the extra adrenaline and the emotions it triggers. Learn about the definition of abnormal anxiety perspectives in mental health. Furthermore they often engage in preconceived maladaptive assumptions that they will behave incompetently in social situations and that their behaviors will lead to terrible consequences.
Other people may have communicated via their actions or the information they provided that certain situations or objects are dangerous and subsequently must be avoid at all costs. Most psychologists would agree that no one approach is correct although in the past in the early days of. Anxiety is the cry of a self in the process of becoming it is expressed through language.
The individual reports fear and worry about a. Behavioural theories were led by John Broadus Watsons experiments on behaviourism that suggested conditioning was responsible for the development of phobias and these ideas were developed by OH. Using a biological perspective a psychologist might look at genetic factors as well as brain processes that might lead to feelings of anxiety.
Psychoanalytic Perspectives On Anxiety. The diagnosis of emotional and mental disorders is anything but arbitrary. Administration of an anti-anxiety drug has a biochemical impact but this.
Scientists and mental health professionals may adopt different perspectives in attempting to understand or explain the underlying mechanisms that contribute to the development of a psychological disorder. Psychological Explanations of Anxiety Disorders Simply having a biological predisposition or a heightened sensitivity to stress is not enough to develop an anxiety disorder. The impact of anxiety on cognitive function is a major contributing factor to these costs.
Individuals with social anxiety disorder tend to hold unattainable or extremely high social beliefs and expectations. There is one central concept to the arguments presented in this paper and it is this. Anxiety is a psychological response to this heightened state of a threat when there is no threat.
Freud placed the experience of anxiety at the core of our psychic functioning - the defining psychic burden of a human being. As previously mentioned a person is more likely to develop an anxiety disorder if they are biologically predisposed to anxiety in conjunction with a psychological vulnerability.
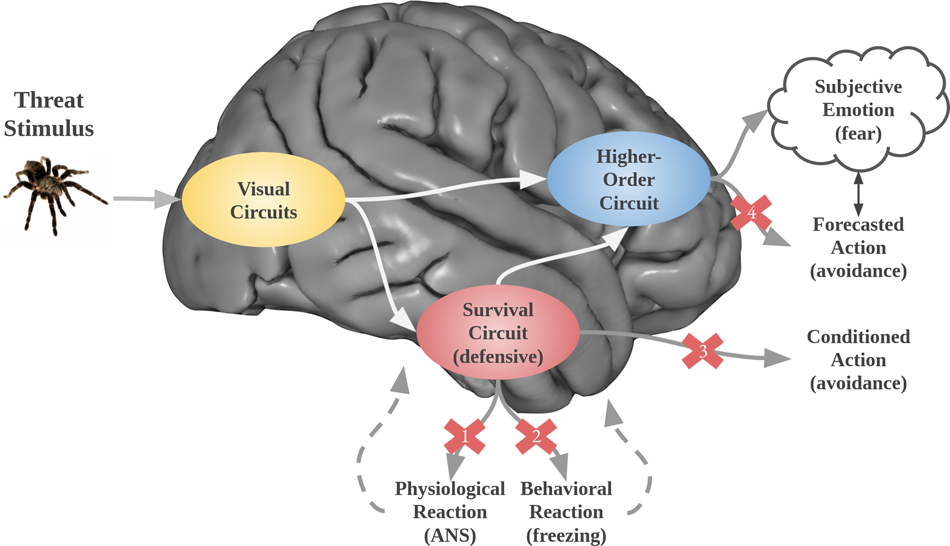
Putting The Mental Back In Mental Disorders A Perspective From Research On Fear And Anxiety Molecular Psychiatry

The Five Psychological Domains Introduction To Psychology
13 1 Psychological Disorder What Makes A Behaviour Abnormal Introduction To Psychology 1st Canadian Edition

Psychological Perspectives List Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
0 Response to "Anxiety Explained in Different Psychological Perspectives"
Post a Comment